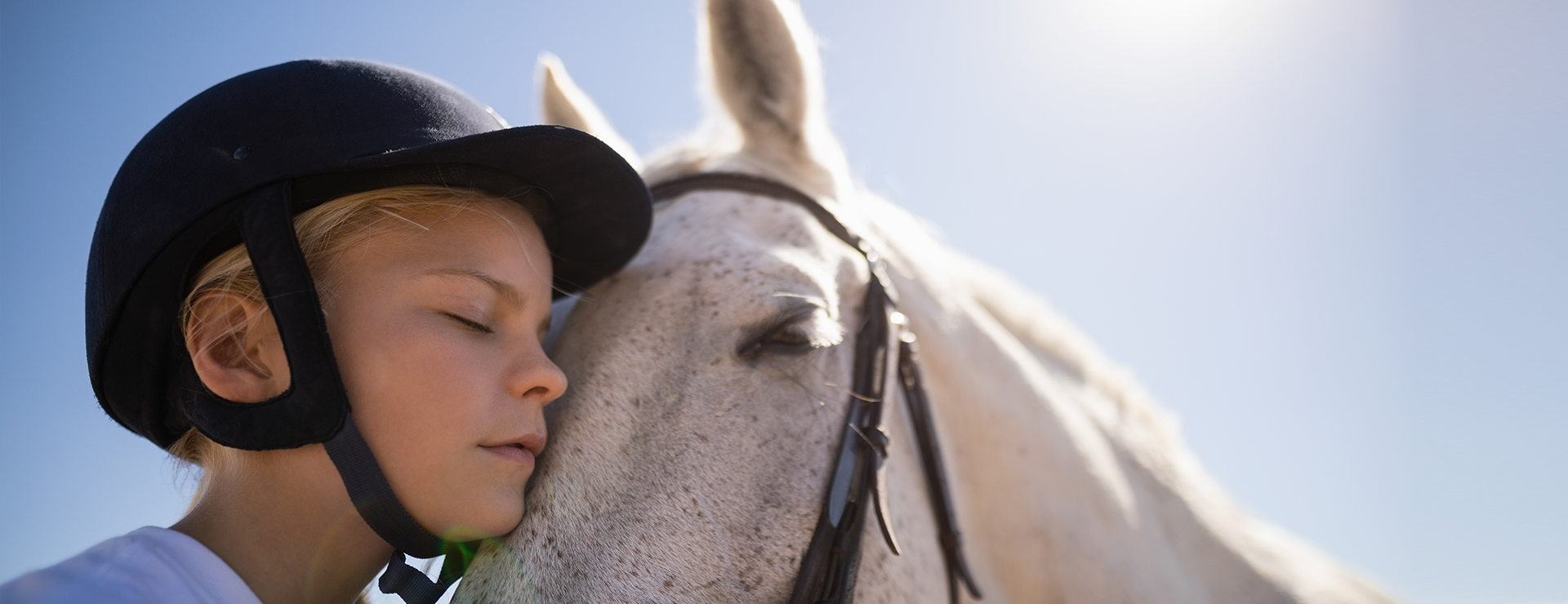
Therapeutic Horseback Riding
While there may not be specific research on the effects of therapeutic horse therapy for individuals with GABA A variants, here are some general reasons why it can be beneficial:
Sensory stimulation and integration: Horseback riding provides a unique sensory experience. The movement of the horse stimulates the vestibular system and provides sensory input through touch, proprioception (awareness of body position), and visual engagement. This can be beneficial for individuals with sensory processing difficulties associated with a GABA A variant, helping to improve sensory integration and regulation.
Postural control and core strength: Riding a horse requires balance and coordination, which can help improve postural control and core strength. The rhythmic movement of the horse’s gait stimulates the muscles and joints, promoting muscle strength and coordination.
Motor coordination and balance: Riding a horse involves coordinated movements and balance adjustments. It can help individuals with motor challenges related to a GABA A variant improve their coordination, spatial awareness, and overall balance.
Emotional and psychological well-being: Interacting with horses can have a positive impact on emotional well-being. Horses are known for their intuitive and non-judgmental nature, which can create a sense of connection, trust, and emotional support. The bond formed between the individual and the horse can promote self-confidence, self-esteem, and reduce anxiety or stress.
Cognitive and attentional skills: Engaging in therapeutic horseback riding requires focus, attention, and following instructions from the instructor or therapist. This can help improve cognitive skills such as attention span, concentration, and task sequencing.
Social interaction and communication: Therapeutic horseback riding often takes place in a group setting, providing opportunities for social interaction and peer engagement. Group activities, games, and shared experiences with other riders can promote social skills, communication, and teamwork.
Motivation and engagement: The engaging and motivating nature of interacting with horses can enhance participation and enjoyment in therapy sessions. The novelty and excitement of riding a horse can increase motivation and make therapy activities more enjoyable and rewarding.
Physical exercise and fitness: Riding a horse involves physical exertion and engagement of various muscle groups. It can provide a form of enjoyable exercise, promoting cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, endurance, and overall physical well-being.
It’s essential to work with a qualified therapeutic riding instructor or equine therapist who has experience working with individuals with diverse needs. They can assess the individual’s specific abilities, set appropriate goals, and design a tailored therapeutic horseback riding program to address their needs and maximize the potential benefits.